China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News: This headline immediately grabs your attention, right? We’re diving deep into how China became the world’s factory floor, exploring its history, current state, and future challenges. We’ll uncover the key policy decisions, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors that shaped this economic powerhouse. Get ready for a fascinating look at a complex and ever-evolving landscape.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News – pretty fascinating stuff, right? It makes you think about the global supply chain, and how even seemingly unrelated things connect. For example, the sheer volume of goods produced likely impacts the availability of, say, the clothes Molly-Mae might wear, as seen in this article: Molly-Mae and Tommy Fury spark reunion rumours as they are.
It’s a reminder that seemingly separate news stories often intertwine within the larger global economic picture, all tied back to China’s manufacturing might.
From its humble beginnings to its current dominance, China’s manufacturing sector has undergone a remarkable transformation. We’ll examine its strengths and weaknesses, the intricate global supply chains it anchors, and the potential risks associated with over-reliance on its production capabilities. We’ll also explore the impact of automation, environmental concerns, and geopolitical shifts on China’s manufacturing future.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News
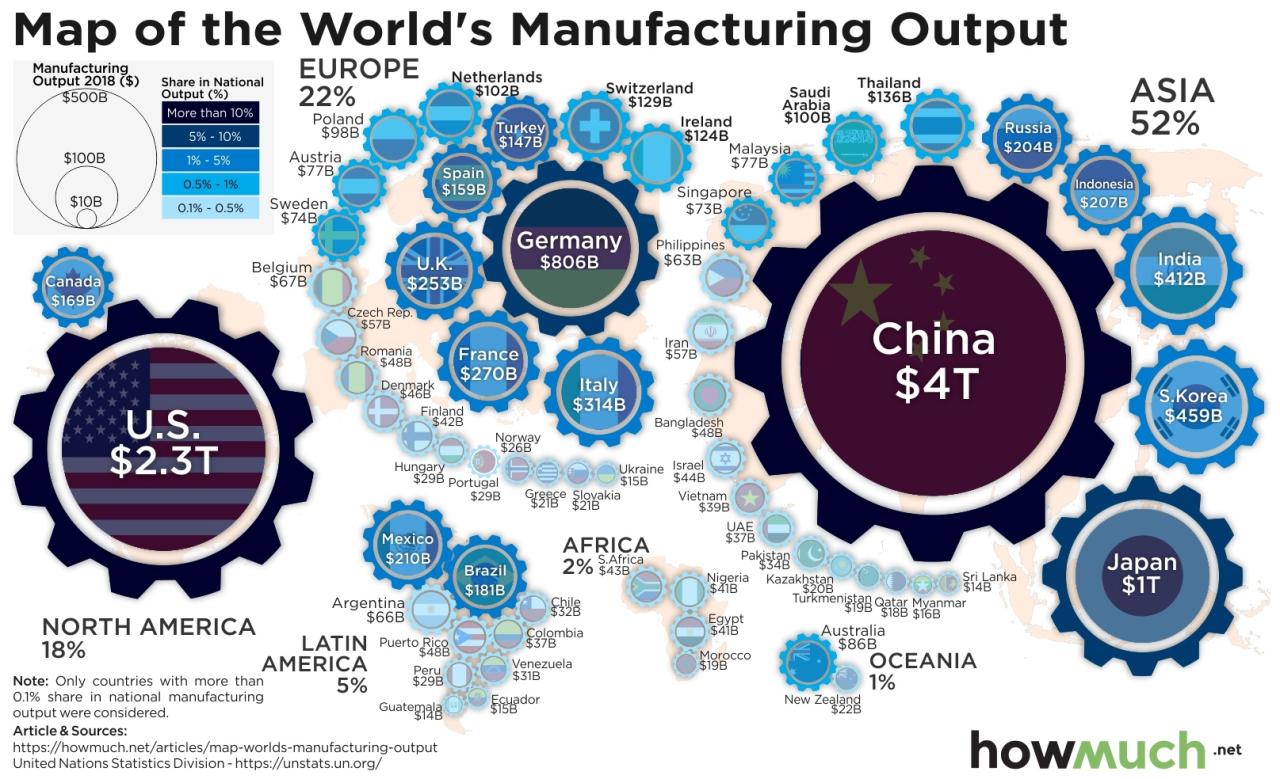
China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a remarkable story of economic transformation. From a largely agrarian economy just a few decades ago, it has become the global factory, dominating numerous industries and deeply integrating itself into global supply chains. This dominance wasn’t accidental; it’s the result of strategic policy decisions, significant investments, and a rapidly evolving workforce.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: Historical Context
China’s manufacturing journey began with modest beginnings, characterized by labor-intensive industries and limited technological capabilities. The implementation of economic reforms in the late 1970s, notably the opening up to foreign investment and the establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs), marked a turning point. These reforms attracted substantial foreign direct investment (FDI), providing access to capital, technology, and management expertise.
Simultaneously, the country’s vast workforce offered a significant cost advantage compared to other manufacturing hubs.
Key policy decisions, such as the prioritization of export-oriented manufacturing and the development of robust infrastructure, further fueled growth. The government also invested heavily in education and vocational training, creating a skilled workforce capable of supporting increasingly sophisticated manufacturing processes. This contrasts sharply with the early industrialization of nations like the US and Great Britain, which relied more on internal markets and had a slower pace of technological adoption.
Comparing China’s manufacturing prowess to other major economies reveals its rapid ascent. While the US, Germany, and Japan had established significant manufacturing sectors earlier, China’s growth trajectory has been exceptional.
| Country | Year | Key Manufacturing Sector | Global Market Share (Illustrative Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 1950 | Automotive, Steel | High (Dominant in many sectors) |
| Germany | 1970 | Automotive, Machinery | High (Strong in specialized industries) |
| Japan | 1980 | Electronics, Automobiles | High (Technological leader in many sectors) |
| China | 2020 | Electronics, Textiles, Machinery | Very High (Dominant in many consumer goods and intermediate goods) |
Note: Global market share figures are illustrative examples and vary widely depending on the specific sector and year.
Current State of Chinese Manufacturing
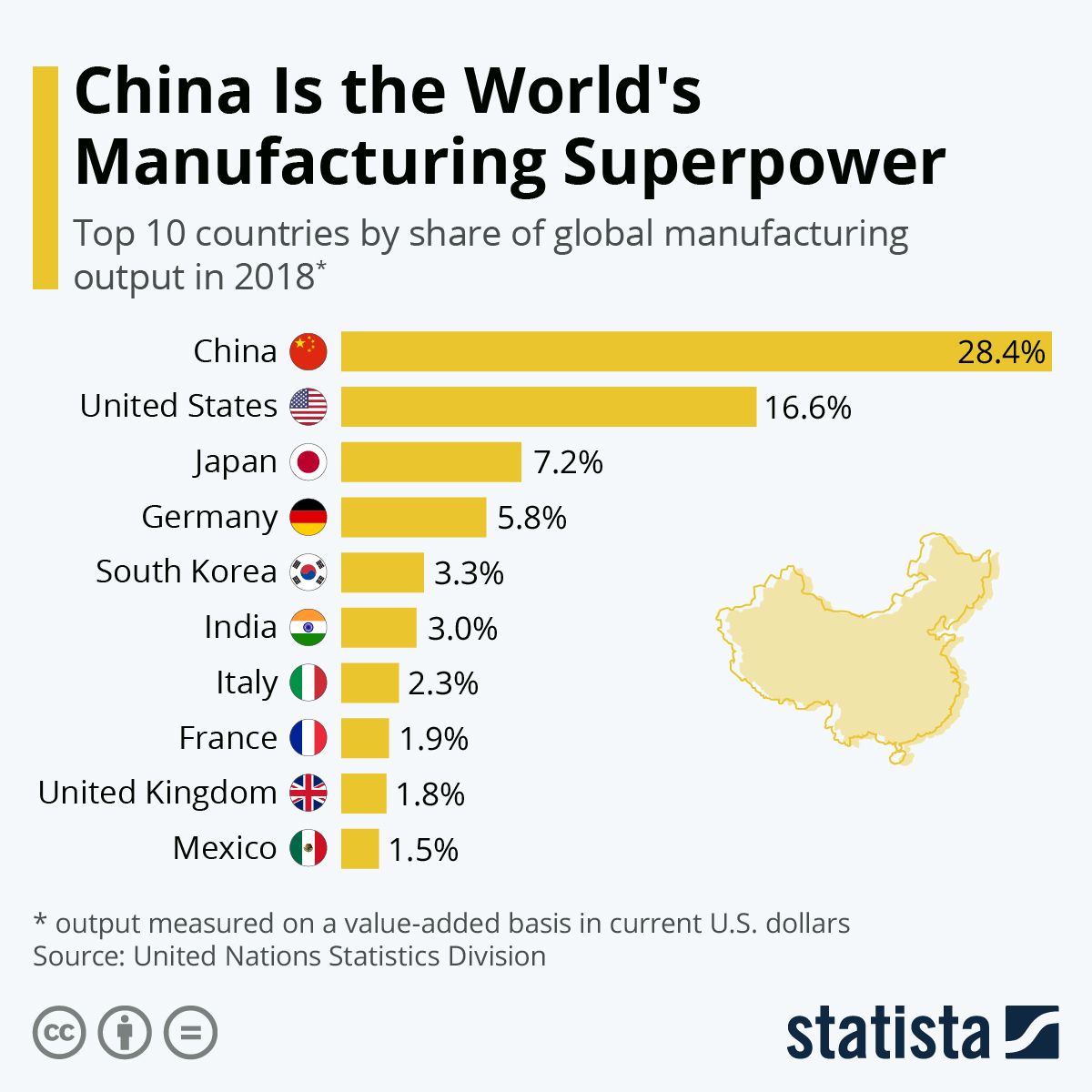
China’s manufacturing sector is incredibly diverse, encompassing a vast array of industries. Its global market share is substantial in many sectors, including electronics, textiles, apparel, footwear, toys, and machinery. However, the landscape is not without its challenges.
- Strengths: Large and skilled workforce, extensive supply chains, cost-effective production, government support, and increasing technological capabilities.
- Weaknesses: Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, dependence on foreign technology in certain areas, and increasing competition from other manufacturing hubs.
- Technology and Automation: China is rapidly adopting automation and advanced technologies such as AI and robotics to improve efficiency and competitiveness. This is driven by both government initiatives and the private sector’s push for greater productivity.
Global Supply Chains and China’s Role
China’s central role in global supply chains is undeniable. Many multinational corporations rely heavily on Chinese manufacturers for components, intermediate goods, and finished products. This reliance creates both opportunities and risks.
The implications of this dependence are far-reaching. Disruptions to Chinese manufacturing, whether due to natural disasters, political instability, or pandemics, can have significant cascading effects on global economies.
| Industry | Dependence on Chinese Manufacturing (Illustrative Example) | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | High (Many components sourced from China) | Supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions |
| Apparel | Very High (Significant manufacturing capacity in China) | Trade wars, labor disputes |
| Automotive | Moderate (Some components and finished vehicles sourced from China) | Geopolitical risks, trade barriers |
Note: The level of dependence is an illustrative example and varies across specific companies and products within each industry.
So you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News – it’s a huge topic! But let’s shift gears for a sec: Check out how the Nipissing Lakers women’s hockey team has high hopes for the upcoming season – a completely different kind of powerhouse! Then, you can dive back into that fascinating Hacker News discussion about China’s global manufacturing influence.
It’s all about perspective!
Challenges and Future Trends in Chinese Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing sector faces several significant challenges that could impact its future dominance. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge.
- Rising Labor Costs: As wages increase, China’s cost advantage diminishes, pushing manufacturers to seek more automated solutions and potentially relocate production to other lower-cost countries.
- Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of China’s manufacturing sector is substantial, leading to increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices.
- Technological Competition: Other countries are investing heavily in their own manufacturing sectors, and technological advancements are leveling the playing field.
- Adaptation Strategies: China can adapt by focusing on higher-value manufacturing, investing in automation and technological innovation, promoting sustainable practices, and developing its domestic consumer market.
The Impact of Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical events significantly influence China’s manufacturing sector. Trade wars, sanctions, and political tensions can disrupt supply chains, impact investment flows, and affect market access.
The impact varies across sub-sectors. For example, sectors heavily reliant on exports to specific countries are more vulnerable to trade disputes. Conversely, sectors focused on the domestic market may be less affected.
A timeline illustrating key geopolitical events and their impact would require a detailed historical analysis beyond the scope of this brief overview.
Technological Advancements and Their Influence, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News
Technological innovation is a key driver of China’s manufacturing growth. Investments in AI, robotics, and 5G are transforming factories, boosting productivity, and improving quality.
Advancements in AI are enabling more efficient production processes, predictive maintenance, and improved quality control. Robotics is automating repetitive tasks, increasing output and reducing labor costs. 5G networks are enabling faster data transfer and real-time monitoring, enhancing factory efficiency.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
The environmental impact of China’s manufacturing sector is a significant concern. Air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation are major challenges.
China is increasingly prioritizing environmental sustainability, implementing policies and initiatives aimed at promoting cleaner production, renewable energy adoption, and waste reduction. However, balancing economic growth with environmental protection remains a complex undertaking.
The Worker Perspective

Working conditions and employment practices in Chinese factories vary widely, ranging from relatively good conditions in some advanced facilities to more challenging conditions in others. Automation and technological advancements are impacting employment, leading to job displacement in some areas and creating new opportunities in others.
Perspectives from workers and labor organizations are diverse, reflecting a range of experiences and concerns related to wages, working hours, safety, and worker rights. Ensuring fair labor practices and providing adequate worker protections are critical aspects of sustainable development in China’s manufacturing sector.
Conclusive Thoughts
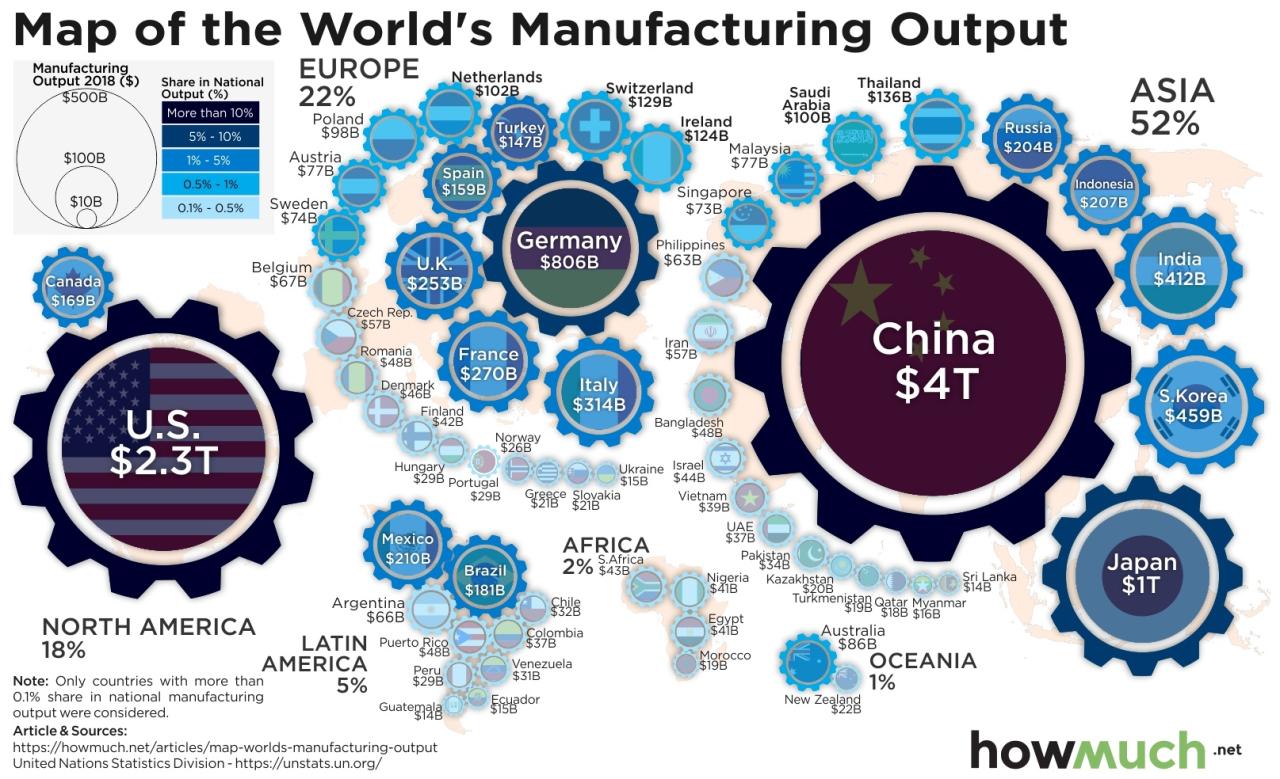
China’s reign as the world’s manufacturing superpower isn’t guaranteed. While its current dominance is undeniable, navigating rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and technological competition will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge. The future will depend on its ability to adapt, innovate, and address the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. The story of China’s manufacturing sector is far from over; it’s a dynamic narrative that continues to unfold, shaping the global economy as it goes.
So, you’re reading about China’s manufacturing dominance on Hacker News? It’s pretty mind-blowing, right? Take a quick break to check out this amazing celestial event – you can see the Venus Moon duo and Quadrantids meteors stun stargazers – before diving back into the complexities of global manufacturing and China’s role in it. Then, get back to that fascinating Hacker News discussion!
Helpful Answers
What are some examples of specific products heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing?
Electronics (smartphones, computers), textiles and clothing, toys, and many components for automobiles are just a few examples.
How is China addressing environmental concerns within its manufacturing sector?
China is implementing stricter environmental regulations, investing in renewable energy sources, and promoting sustainable manufacturing practices, though challenges remain.
What is the impact of automation on Chinese manufacturing workers?
Automation is leading to job displacement in some areas, but also creating new roles requiring higher skills. The overall impact on employment is complex and still evolving.